Intel Pentium D / Intel Pentium Extreme Edition
 Die Entwicklung der immer schneller getakteten Prozessoren hat bei Intel ein rapides Ende genommen. Die magische Grenze von 4 GHz hat der Pentium 4 nicht erreicht. Zu groß war die Verlustleistung und die daraus entstehende Wärmeenergie, die sich durch kaum eine Kühlmaßnahme in den Griff bekommen ließ. Auch die Reduzierung von Prozessortakt und -spannung zur Laufzeit führte nicht zum gewünschten Ergebnis. Der Wunsch seitens der Anwender nach leisen und kleineren Systemen konnte auch Intel nicht ignorieren und zwang zum Umdenken.
Die Entwicklung der immer schneller getakteten Prozessoren hat bei Intel ein rapides Ende genommen. Die magische Grenze von 4 GHz hat der Pentium 4 nicht erreicht. Zu groß war die Verlustleistung und die daraus entstehende Wärmeenergie, die sich durch kaum eine Kühlmaßnahme in den Griff bekommen ließ. Auch die Reduzierung von Prozessortakt und -spannung zur Laufzeit führte nicht zum gewünschten Ergebnis. Der Wunsch seitens der Anwender nach leisen und kleineren Systemen konnte auch Intel nicht ignorieren und zwang zum Umdenken.
Doppelkern- bzw. Mehrkernprozessoren sind eine neue Strategie, die die Firmen Intel und AMD in ihren Entwicklungsabteilungen verfolgen.
Zur Einführung seiner Dualcore-Prozessoren hatte Intel den Pentium Extreme Edition 840XE und den Pentium D angekündigt.
Architektur des Pentium D und Pentium Extreme Edition
| Intel Pentium D | Intel Pentium Extreme Edition |
|---|---|
 |
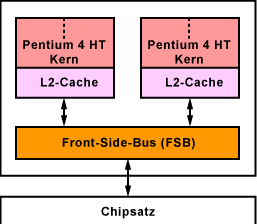 |
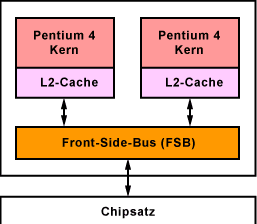
Beide Prozessor-Modelle enthalten zwei Pentium-4-Kerne (Prescott) mit jeweils 1 MByte L2-Cache. Beide Kerne haben einen gemeinsamen Bus zum Chipsatz und teilen sich somit die gesamte Bandbreite des Front-Side-Bus (FSB) mit 800 MHz. Die beiden neuen Prozessoren haben 230 Millionen Transistoren, was die Leistungsaufnahme enorm steigert und die Kühlung der Prozessoren erschwert. Deshalb sind die Prozessoren um 600 MHz langsamer getaktet, als die Singlecore-Prozessoren.
Der Pentium D und der Pentium Extreme Edition (ohne 4) befinden sich in einem LGA775-Gehäuse. Beide beherrschen die 64-Bit-Befehlssatzerweiterung EM64T. Der Pentium D, als direkter Nachfolger des Pentium 4, unterstützt kein Hyper-Threading (HT). Der Pentium Extreme Edition dagegen schon. Er besteht aus vier virtuellen Prozessorkernen.
Prozessor-Übersicht:
Stand: 17.03.2008
| Modell | Kerne | Kerntakt | L2-Cache | FSB | Sonstiges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Pentium D (Kern: Smithfield), 140 mm², 90 nm, LGA775 | |||||
| 805 | 2 | 2,66 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 533 MHz | EM64T, NX |
| 820 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 533 MHz | EM64T, NX |
| 820 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX |
| 830 | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, EIST |
| 840 | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, EIST |
| Intel Pentium Extreme Edition (Kern: Smithfield), 90 nm | |||||
| 840 XE | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | 800 MHz | HT, EM64T, NX, EIST |
| Intel Pentium D (Kern: Presler), 140 mm², 376 Mio. Transistoren, 65 nm, LGA775 | |||||
| 915 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 920 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT |
| 920 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT, C1E, EIST |
| 925 | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 930 | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT |
| 930 | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT, C1E, EIST |
| 935 | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 940 | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT |
| 940 | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT, C1E, EIST |
| 945 | 2 | 3,4 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 950 | 2 | 3,4 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT |
| 950 | 2 | 3,4 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 950 | 2 | 3,4 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT, C1E, EIST |
| 960 | 2 | 3,6 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, C1E, EIST |
| 960 | 2 | 3,6 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 800 MHz | EM64T, NX, VT, C1E, EIST |
| Intel Pentium Extreme Edition (Kern: Presler), 65 nm | |||||
| 955 | 2 | 3,46 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 1066 MHz | HT, EM64T, NX, VT |
| 965 | 2 | 3,73 GHz | 2 x 2 MByte | 1066 MHz | HT, EM64T, NX, VT |
Vergleich: Vom Pentium bis Pentium D
| Pentium | Pentium MMX | Pentium Pro | Pentium II | Pentium III | Pentium 4 | Pentium D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transistoren | 3,3 Mio. | 4,5 Mio. | 5,5 Mio | bis 9 Mio. | bis 44 Mio. | bis 188 Mio. | bis 376 Mio. |
| Level-1-Cache | 8 KB Daten 8 KB Code |
16 KB Daten 16 KB Code |
8 KB Daten 8 KB Code |
16 KB Daten 16 KB Code |
16 KB Daten 16 KB Code |
16 KB Daten 16 KB Code |
- |
| Level-2-Cache | - | - | 256 / 512 kByte | 512 kByte | 256 / 512 kByte | 256 / 512 / 1024 / 2048 kByte | 2 x 1024 / 2 x 2048 kByte |
| MMX/SSE | nein | ja | nein | ja | ja | ja | ja |
| Befehle pro Takt | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | - | - | - |
| Taktfrequenzen | 60 - 200 MHz | 166 - 233 MHz | 150 - 200 MHz | 233 - 450 MHz | 450 - 1400 MHz | 1,3 - 3,8 GHz | 2,66 - 3,73 GHz |
| Front-Side-Bus | 60/66 MHz | 66 MHz | 66 MHz | 66/100 MHz | 100/133 MHz | 400/533/800 quadpumped | 533/800/1066 quadpumped |
| Sockel | Sockel-5 | Sockel-7 | Sockel-8 | Slot-1 | Slot-1 / S370 | S428 / S478 / LGA775 | LGA775 |