AMD Athlon (64) X2
 Im April 2005 wurden die Doppelkern-Prozessoren von AMD veröffentlicht. Nahezu gleichzeitig hat Intel seine Doppelkern-Prozessoren präsentiert.
Im April 2005 wurden die Doppelkern-Prozessoren von AMD veröffentlicht. Nahezu gleichzeitig hat Intel seine Doppelkern-Prozessoren präsentiert.
Der AMD Athlon 64 X2 ist der Nachfolger des Athlon 64 FX.
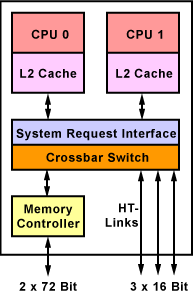
Bei der Konzeption des AMD64-Kerns hat AMD gleich auf Dual-Core-Fähigkeit geachtet. Beide Kerne sind mit je 128 kByte L1-Cache und je nach Kern mit 512 kByte oder 1 MByte L2-Cache ausgestattet. Über einen eigenen Kanal kann ein Kern den Status einer Cache-Zelle des anderen Kerns abfragen, ohne dass der restliche Datenverkehr ausgebremst wird.
Beide Kerne greifen auf den gemeinsamen Crossbar-Switch zu, über den sie Verbindung zum Memory-Controller haben. Drei HyperTransport-Links sind die Verbindung zum Chipsatz.
Als Sockel dient der S939. Mit einem BIOS-Update kann der Athlon 64 X2 in modernen Motherboards verwendet werden.
Seit Mai 2006 gibt es den Athlon 64, Athlon 64 X2 und Sempron mit dem AM2-Sockel und DDR2-Speicherinterface. Für manche Prozessor-Modelle gibt es auch spezielle stromsparende Typen (EE und EE SFF).
Der AMD Athlon 64 X2 und der AMD Athlon X2 sind praktisch die gleichen Prozessoren. Bei letzterem hat AMD irgendwann die "64" weg gelassen.
Besonderheit: Speichertakt
Mit dem Umstieg zum AM2-Sockel verwendet AMD DDR2-Speicher. Während DDR-Speicher noch mit 200 MHz getaktet war, beträgt der Speichertakt von DDR2-Speicher 400 MHz. Der Speichertakt ergibt sich aus dem CPU-Takt. Dabei wird der Kerntakt durch einen ganzzahligen Teiler geteilt. Der richtige Teiler ist es dann, wenn der Speichertakt nicht größer als 400 MHz ist.
Um von 2200 MHz eines Athlon 64 X2 4400+ auf 400 MHz Speichertakt zu kommen würde der Teiler 5,5 sein. Da aber nur ganzzahlige Teiler verwendet werden dürfen, kommt der nächsthöhere Teiler von 6 in Frage. Das bedeutet, dass der Speichertakt nicht 400 MHz, sondern nur 367 MHz beträgt. Die DDR-Speicher mit nur 200 MHz hatten dieses Problem nicht.
NPT - New Plattform Technology
AMD spricht bei Prozessoren mit integriertem DDR2-Speichercontroller von der "New Plattform Technology". Das betrifft alle Prozessoren im AM2- und LGA1207-Gehäuse. Nur diese AMD64-Prozessoren unterstützen die Befehlssatzerweiterung AMD-V, Die Virtualisierungsfunktionen Secure Virtual Maschine (SVM), die unter dem Codenamen Pacifica bekannt ist, und dem Speicher-Zugriffsschutz (Presidio).
Prozessor-Übersicht: AMD Athlon 64 X2
Hinweis: Das Namensschema der AMD-Prozessoren ist ein Wildwuchs von Zahlen mit und ohne Plus, mit angehängtem "e" oder "B" und vorneweg mit LE oder BE.
Der AMD Athlon X2 Black Edition (BE) ist ein normaler Prozessor, dessen Multiplikator frei einstellbar ist und sich damit einfacher übertakten lässt.
Kurzzeitig verwendete AMD für den Athlon 64 X2 ein verwirrendes Bezeichnungssystem. Allerdings haben die Kunden dagegen interveniert. Deshalb kehrte AMD schnell wieder zur alten und bewährten Bezeichnungssystem zurück.
Die AMD-Prozessoren für die Embedded-Baureihe erkennt man an dem kleinen "e" in der Prozessor-Bezeichnung. Diese Prozessoren sind sparsame Desktop-Prozessoren mit 15 oder 22 Watt. Sie eignen sich auch für Embedded- und Industrie-PCs.
Stand: 06.06.2009
| Name | Kerne | Kerntakt | L2-Cache | L3-Cache | Sockel | Besonderheiten |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 (Kern: Manchester), 90 nm | ||||||
| 3800+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4200+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4600+ | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 (Kern: Toledo), 90 nm | ||||||
| 3800+ | 2 | 2,0 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4200+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4400+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4600+ | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | S939 | - |
| 4800+ | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | S939 | - |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 (Kern: Windsor), 218 mm², 228 Mio. Transistoren, 90 nm | ||||||
| 3600+ (EE) | 2 | 2,0 GHz | 2 x 256 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 3800+ (EE SFF) | 2 | 2,0 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 4000+ (EE) | 2 | 2,0 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 4200+ (EE) | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 4400+ (EE) | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 4600+ (EE) | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 4800+ (EE) | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 5000+ | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 5200+ (EE) | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 5400+ | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 5600+ | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 6000+ | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| 6400+ (BE) | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| FX-62 | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | AM2 | SVM |
| FX-70 | 4 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | LGA1207 | SVM |
| FX-72 | 4 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | LGA1207 | SVM |
| FX-74 | 4 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 1 MByte | - | LGA1207 | SVM |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 (Kern: Brisbane), 118 mm², 221 Mio. Transistoren, 65 nm | ||||||
| 3600+ | 2 | 1,9 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| 3800+ | 2 | 2,1 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| 4000+ | 2 | 2,1 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| 4200+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| 4400+ | 2 | 2,3 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 (Kern: Regor), 45 nm | ||||||
| 500+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |
Prozessor-Übersicht: AMD Athlon X2
Stand: 06.06.2009
| Name | Kerne | Kerntakt | L2-Cache | L3-Cache | Sockel | Besonderheiten |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Athlon X2 (Kern: Brisbane), 118 mm², 221 Mio. Transistoren, 65 nm | ||||||
| BE-2300 | 2 | 1,9 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| BE-2350 | 2 | 2,1 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| BE-2400 | 2 | 2,3 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | - |
| 4050e | 2 | 2,1 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4450e | 2 | 2,3 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4450B | 2 | 2,3 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4200+ | 2 | 2,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4400+ | 2 | 2,3 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4800+ | 2 | 2,5 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 4850e | 2 | 2,5 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5000B | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5000+ (BE) | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5050e | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5200+ | 2 | 2,7 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5200B | 2 | 2,7 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5400+ | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5400B | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5600+ | 2 | 2,9 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 5800+ | 2 | 3,0 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 6000+ | 2 | 3,1 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 6400 | 2 | 3,2 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| 6500 (BE) | 2 | ? | 2 x 512 kByte | - | AM2 | AMD-V |
| AMD Athlon X2 (Kern: Kuma), 283 mm², 463 Mio. Transistoren, 65 nm | ||||||
| 7450 | 2 | 2,4 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | 2 MByte | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |
| 7550 | 2 | 2,5 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | 2 MByte | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |
| 7650 | 2 | 2,6 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | 2 MByte | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |
| 7750 BE | 2 | 2,7 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | 2 MByte | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |
| 7850 BE | 2 | 2,8 GHz | 2 x 512 kByte | 2 MByte | AM2+ | SSE128, AMD-V |